Reference¶
- Author:
Pauli Virtanen <pauli@ltl.tkk.fi>
- Organization:
Low Temperature Laboratory, Helsinki University of Technology
- Date:
2005-2006
A solver for Keldysh-Usadel 1D circuit equations.
To find out how this library can be used, you should peek at
solver.Geometry: How to specify a geometry
currents: Simple interface to calculating currents
selfconsistentiteration: A self-consistent iteration
solver: Low-level solver interface
Geometry¶
- class usadel1.Geometry(nwire, nnode, x=None)¶
Geometry of the setup.
- Parameters:
- nwireint
Number of wires in the setup
- nnodeint
Number of nodes in the setup
- xarray of floats, optional
Array of x-positions at which quantities are specified. These must be in the range [0, 1].
Examples
A three-probe structure:
3 0 S----*----S 1 0 | 1 | |2 | N 2 >>> import numpy as np >>> g = Geometry(nwire=3, nnode=4) >>> g.t_type = [NODE_CLEAN_S_TERMINAL, ... NODE_CLEAN_S_TERMINAL, ... NODE_CLEAN_N_TERMINAL, ... NODE_CLEAN_NODE] >>> g.w_type = WIRE_TYPE_N >>> g.w_ends[0,:] = [0, 3] >>> g.w_ends[1,:] = [1, 3] >>> g.w_ends[2,:] = [2, 3] >>> g.w_length = [0.5, 0.5, 2] >>> g.t_delta = [100, 100, 0, 0] >>> g.t_phase = np.array([-.5, .5, 0, 0]) * np.pi/2 >>> g.t_t = 1 >>> g.t_mu = 0
- property coupling_lambda¶
array(nwire, nx) of
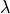 in wires
in wires
- equal(other, compare_delta=True, compare_kinetic=True, compare_phases=True)¶
Compare two geometries.
Parameters
- otherGeometry
The geometry to compare this one to.
- compare_kineticbool, optional
Whether to compare kinetic quantities (temperatures, potentials)
- compare_deltabool, optional
Whether to compare
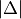 between the Geometries.
between the Geometries.- compare_phasesbool, optional
Whether to compare
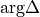 between the Geometries.
between the Geometries.
- get_idstr()¶
Get a descriptive string for this geometry.
- get_node_wires()¶
Collect lists of wires connected to each node, and label nodes by which end of the wires they correspond to.
- property nnode¶
how many nodes in geometry
- property nwire¶
how many wires in geometry
- property omega_D¶
array(nwire, nx) of Debye frequency in wires
- property t_delta¶
array(nnode) of energy gaps of nodes
- property t_inelastic¶
array(nnode) of
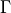 -s of nodes
-s of nodes
- property t_mu¶
array(nnode) of node potentials
- property t_phase¶
array(nnode) of phases of nodes
- property t_resistance¶
array(nnode) of node resistances
Has effect only for NODE_TUNNEL_* nodes.
- property t_spinflip¶
FIXME: this is not yet functional array(nnode) of
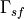 -s of node
-s of node
- property t_t¶
array(nnode) of node temperatures
- property t_type¶
array(nnode) of types of nodes
Possible choices are: NODE_CLEAN_N_TERMINAL (normal terminal; clean interface), NODE_CLEAN_S_TERMINAL (superconducting terminal; clean interface), NODE_CLEAN_NODE (node connecting several wires; clean interface), NODE_FREE_INTERFACE (vacuum interface).
- property w_conductance¶
array(nwire) of conductance*area of wires
- property w_delta¶
array(nwire, nx) of energy gaps in wires
- property w_ends¶
array(nwire,2) that maps wire ends -> nodes
- property w_inelastic¶
array(nwire) of
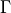 -s of wires
-s of wires
- property w_length¶
array(nwire) of wire lengths
- property w_phase¶
array(nwire, nx) of phase in wires
- property w_phase_jump¶
array(nwire) phase jump between the ends of the wire, due to vector potential parallel to the wire.
- property w_spinflip¶
array(nwire) of
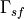 -s of wires
-s of wires
- property w_type¶
array(nwire) of wire types
Possible choices are: WIRE_TYPE_N (normal wire) and WIRE_TYPE_S (superconducting wire).
- property x¶
array(nx) of discretization points.
NOTE: These must be in the range [0,1] !
Note also that this does not affect the actual mesh chosen by all solvers – however, it always affects the discretization used for spectral solutions and kinetic coefficients.
Solver¶
- class usadel1.Solver¶
Low-level interface to the Usadel solver.
- set_geometry(g, preserve=False)¶
Set the geometry to use.
- Parameters:
- gGeometry
The geometry to use
- preservebool, optional
Whether to preserve currently set values for
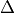 and the kinetic coefficients.
and the kinetic coefficients.
- set_kinetic(coefs)¶
Set the coefficients for the kinetic equations.
- Parameters:
- coefsKineticCoefficients
Kinetic coefficients for the equations.
- sp_solve(E, x, continued=False)¶
Solve spectral equations.
- Parameters:
- Earray of floats
Energies to solve the equations at
- xarray of floats, optional
Positions to return quantities at. Defaults to the same as those in Geometry.
- continuedbool, optional
Whether to use old solution as a starting point.
- Returns:
- solSpResult
Solution to the equations.
- kin_solve(E, x, continued=False)¶
Solve kinetic equations.
- Parameters:
- Earray of floats
Energies to solve the equations at
- xarray of floats, optional
Positions to return quantities at. Defaults to the same as those in Geometry.
- continuedbool, optional
Whether to use old solution as a starting point.
- Returns:
- solKinResult
Solution to the equations.
Results¶
- class usadel1.SpResult(E=None, x=None, r=None)¶
The result from a spectral calculation.
The parameters a and b correspond to the representation
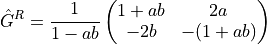
of the retarded Green function.
- Attributes:
- Earray of floats, shape (ne,)
Energies the solutions are evaluated at
- xarray of floats, shape (nx,)
Positions the solutions are evaluated at; scaled to [0, 1]
- aarray of floats, shape (ne, nwire, nx)
Riccati parameter a
- barray of floats, shape (ne, nwire, nx)
Riccati parameter b
- daarray of floats, shape (ne, nwire, nx)
Derivative of a
- dbarray of floats, shape (ne, nwire, nx)
Derivative of b
- neint
Number of energy points
- nxint
Number of x-points
- nwireint
Number of wires
- class usadel1.KinResult(E=None, x=None, r=None)¶
The result from a kinetic calculation.
- Attributes:
- Earray of floats, shape (ne,)
Energies the solutions are evaluated at
- xarray of floats, shape (nx,)
Positions the solutions are evaluated at; scaled to [0, 1]
- fLarray of floats, shape (ne, nwire, nx)
The distribution function
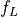
- fTarray of floats, shape (ne, nwire, nx)
The distribution function
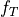
- dfLarray of floats, shape (ne, nwire, nx)
Derivative of fL
- dfTarray of floats, shape (ne, nwire, nx)
Derivative of fT
- jLarray of floats, shape (ne, nwire, nx)
The spectral current
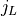
- jTarray of floats, shape (ne, nwire, nx)
The spectral current
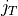
- neint
Number of energy points
- nxint
Number of x-points
- nwireint
Number of wires
- class usadel1.KineticCoefficients(g=None, r=None, to_evaluate=None)¶
Coefficients in the kinetic equations.
- Attributes:
- xarray of floats, shape (nx,)
x-positions the coefficients are evaluated at; scaled to range [0, 1]
- Earray of floats, shape (ne,)
Energies the coefficients are evaluated at
- DLarray, shape (ne, nwire, nx)
Coefficient
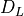
- DTarray, shape (ne, nwire, nx)
Coefficient
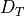
- TTarray, shape (ne, nwire, nx)
Coefficient
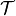
- rjEarray, shape (ne, nwire, nx)
Coefficient
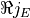
- ijEarray, shape (ne, nwire, nx)
Coefficient
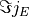
- dDLarray, shape (ne, nwire, nx)
Derivative of DL
- dDTarray, shape (ne, nwire, nx)
Derivative of DT
- dTTarray, shape (ne, nwire, nx)
Derivative of TT
- drjEarray, shape (ne, nwire, nx)
Derivative of rjE
- dijEarray, shape (ne, nwire, nx)
Derivative of ijE
- cTLarray, shape (ne, nwire, nx)
prefactor of
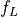 in the sink term for
in the sink term for 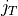
- cTTarray, shape (ne, nwire, nx)
prefactor of
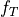 in the sink term for
in the sink term for 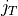
Currents¶
- class usadel1.CurrentSolver(geometry, E=None, chunksize=None, output_function=None, automatic_energy=False, maxE=None, ne=None)¶
Solver for currents flowing in a given geometry.
- Parameters:
- geometryGeometry
The geometry to solve for
- Earray of floats, optional
Energy points to evaluate all quantities at. If omitted, the default is to use a sensibly chosen grid.
- maxEfloat, optional
If E is omitted: the maximum energy for the automatic energy grid.
- neint, optional
If E is omitted: the number of energy points to use.
- automatic_energybool, optional
Whether to choose an energy grid automatically. (Yes, if E is omitted.)
- chunksizeint
How often to display the progress of calculation.
- output_functionfunc(message)
Function to use to print any output. If omitted, print to stderr
- Attributes:
- geometryGeometry
Current geometry
- spectralSpResult
Solution to the spectral equation
- kineticKinResult
Solution to the kinetic equations
- coefficientKineticCoefficient
Coefficients in the kinetic equations
- solverSolver
The low-level solver.
- Garray of floats, shape (ne, nw, 2, 2, nnode)
The spectral conductance/thermoelectric matrix. See eg. [1].
References
Solving equations
- solve()¶
Solve both spectral and kinetic equations.
- solve_spectral()¶
Solve the spectral equations.
Store the results to self.spectral and self.kinetic.
- solve_kinetic(E=None, ne=None)¶
Solve the kinetic equations and store the result to self.kinetic.
- Parameters:
- Earray of floats, optional
The energy discretization to use. None indicates that use either the same as for spectral, or, if self.automatic_energy is
True, pick a sensible choice.- neint, optional
How many points to use in energy discretization, if choosing the energy discretization automatically.
- solve_spectral_if_needed(calculate_G=True)¶
Solve for spectral data if there is none yet.
- Parameters:
- calculate_Gbool, optional
Whether to calculate the spectral conductance/thermoelectric matrix.
- solve_spectral_and_save_if_needed(filename, calculate_G=True, **kw)¶
Solve for spectral data if there is none yet, and save the result to a file.
- Parameters:
- filenamestr
Name of the file to solve data to.
- calculate_Gbool, optional
Whether to calculate the spectral conductance/thermoelectric matrix.
Other parameters as in save.
- calculate_G(superconductors_in_equilibrium=False, only_terminals=None)¶
Compute the spectral conductance matrix.
Warning
Spectral quantities (such as G) are not conserved in superconducting wires. Be aware that the G is evaluated at x[0] in each wire.
- Parameters:
- superconductors_in_equilibriumbool, optional
Assume superconductors are at equilibrium, and skip calculating the conductance matrix entries for them.
- only_terminalslist of int, optional
Terminals for which to calculate the conductance matrix entries. If omitted, calculate for all terminals.
- approximate_G(use_jS=True, use_T=True)¶
Find an approximation for the G-matrix, up to first order in
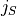 and
and 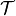 .
.Stores the result to self.G.
- Parameters:
- use_jSbool, optional
Use the spectral supercurrent in the approximation.
- use_Tbool, optional
Use the coefficient
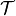 in the approximation.
in the approximation.
- set_solvers(*args, **kwargs)¶
Set solver types and tolerances.
- Parameters:
- sp_solverint, optional
Spectral solver to use. Choices are
SP_SOLVER_COLNEW(default) andSP_SOLVER_TWPBVP.- sp_tolfloat, optional
Tolerance to use in the spectral solver.
- kin_solverint, optional
Kineticsolver to use. Choices are
KIN_SOLVER_COLNEWandKIN_SOLVER_TWPBVP(default), andKIN_SOLVER_BLOCK.- kin_tolfloat, optional
Tolerance to use in the kinetic solver.
Computing currents
- get_currents(E=None, ix=None, w_jL=None, w_jT=None, ne=None)¶
Calculate currents, using fixed-grid discretization.
- Parameters:
- ixint, optional
Index of position to evaluate currents at in each wire. If omitted, current is evaluated at all positions.
- w_jTlist of int, optional
For which wires to compute charge current for. If omitted, compute for all wires.
- w_jLlist of int, optional
For which wires to compute energy current for. If omitted, compute for all wires.
- neint, optional
How many points to put in energy discretization, if chosen automatically.
- Returns:
- Icarray of floats, shape (nwire, nx’)
Charge current in each wire. Contains nan in entries that were not calculated. If ix was given, nx’ == 1, otherwise nx’ == nx.
- IEarray of floats, shape (nwire, nx’)
Energy current in each wire.
- get_currents_lazy(w_jL=None, w_jT=None, epsabs=None, epsrel=None, ix=None)¶
Calculate currents, using an adaptive integrator.
Will solve kinetic equations at energy points where the solutions are needed.
- Parameters:
- epsabsfloat, optional
Absolute tolerance for the currents.
- epsrelfloat, optional
Relative tolerance for the currents.
Also takes the same parameters as get_currents.
- Returns:
Returns similar output as get_currents.
- get_currents_from_G(*args, **kw)¶
Calculate currents, from the spectral conductance matrix.
- Parameters:
- w_jTlist of int, optional
For which wires to compute charge current for. If omitted, compute for all wires.
- w_jLlist of int, optional
For which wires to compute energy current for. If omitted, compute for all wires.
- Returns:
- Icarray of floats, shape (nwire,)
Charge current in each wire. Contains nan in entries that were not calculated.
- IEarray of floats, shape (nwire,)
Energy current in each wire.
- get_currents_from_G_with_f(f_func, w_jT=None, w_jL=None, ix=None)¶
Calculate currents from the G-matrix, for given distribution functions at the terminals.
- Parameters:
- f_funcfunc(E, mu, T)
Function that takes an energy grid of shape (ne, 1) and potentials and temperatures [shape (1, nnode)] and returns (fL, fT) where each entry is an array of shape (ne, nnode) describing the distribution function at each energy in each terminal.
- w_jTlist of int, optional
For which wires to compute charge current for. If omitted, compute for all wires.
- w_jLlist of int, optional
For which wires to compute energy current for. If omitted, compute for all wires.
- Returns:
- Icarray of floats, shape (nwire,)
Charge current in each wire. Contains nan in entries that were not calculated.
- IEarray of floats, shape (nwire,)
Energy current in each wire.
Computing linear response
- get_linear_response_from_G(*args, **kw)¶
Compute the linear response in currents to changes in potentials and temperatures in the terminals.
This function assumes that the distribution function in each terminal is a Fermi function.
- Parameters:
- w_jTlist of int, optional
For which wires to evaluate the charge current related entries.
- w_jLlist of int, optional
For which wires to evaluate the energy current related entries.
- Returns:
- G_VVarray, shape (nwire, nnode)
Conductance matrix; contains entries
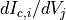 .
Has nan at entries that were not calculated.
.
Has nan at entries that were not calculated.- G_VTarray, shape (nwire, nnode)
Thermoelectric matrix; contains entries
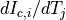 .
.- G_TVarray, shape (nwire, nnode)
Thermoelectric matrix; contains entries
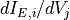 .
.- G_TTarray, shape (nwire, nnode)
Thermal conductance matrix; contains entries
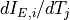 .
.
- get_linear_response_from_G_with_f(df_func, w_jT=None, w_jL=None)¶
Compute the linear response in currents to changes in distribution functions in the terminals.
- Parameters:
- df_funcfunc(E, mu, T)
Function that takes an energy grid of shape (ne, 1) and potentials and temperatures [shape (1, nnode)] and returns (dfL_dT, dfL_dV, dfT_dT, dfT_dV) where each entry is an array of shape (ne, nnode) describing the change in the distribution function with regard to perturbation in each parameter.
- w_jTlist of int, optional
For which wires to evaluate the charge current related entries.
- w_jLlist of int, optional
For which wires to evaluate the energy current related entries.
- Returns:
- G_VVarray, shape (nwire, nnode)
Conductance matrix; contains entries
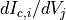 .
Has nan at entries that were not calculated.
.
Has nan at entries that were not calculated.- G_VTarray, shape (nwire, nnode)
Thermoelectric matrix; contains entries
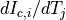 .
.- G_TVarray, shape (nwire, nnode)
Thermoelectric matrix; contains entries
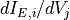 .
.- G_TTarray, shape (nwire, nnode)
Thermal conductance matrix; contains entries
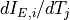 .
.
Saving and loading data:
- classmethod load(src, path=None, **kw)¶
Load data from an open HDF5 file.
- Parameters:
src: a tables.Group where to load data from, or a file name joined with node path.
Other arguments (except
geometry) are passed on to __init__
- save(to, path=None, save_coefficient=True, save_spectral=True, save_kinetic=True)¶
Save date to an open HDF5 file.
- Parameters:
- to: str or tables.File
A file name or a parent HDF5 node to save to
- pathstr, optional
HDF5 name to save under
- save_coefficientbool, optional
Whether to save kinetic coefficients
- save_spectralbool, optional
Whether to save spectral data
- save_kineticbool, optional
Whether to save kinetic data.
Notes
Geometry is saved in all cases.
- classmethod resume(src, geometry, path=None, compare_E=False, **kw)¶
Load data from a data file if parameters match or return a new solver if not.
Optimizing parameters¶
- usadel1.optimize_parameters_for(x0, zero_func, adjust_func, **kwargs)¶
Find a configuration where the specified quantity vanishes, by adjusting the specified variables.
- Parameters:
- x0array
Initial guess for all n parameters
- zero_funcfunc()
Function whose zero to look for; should return a vector of the same size as x0.
- adjust_funcfunction(x)
Function to call to set current parameters
Other keyword arguments accepted by scipy.optimize.fsolve can be given.
Notes
If AlreadyConvergedException is raised by zero_func, the optimization terminates successfully with the current value.
- exception usadel1.AlreadyConvergedException¶
An exception that the user can raise during optimize_parameters_for to indicate that the optimum has been already reached.
Self-consistent iteration¶
- usadel1.self_consistent_realtime_iteration(currents, max_iterations=100, output_func=<built-in method write of _io.TextIOWrapper object>, iterator=<class 'usadel1.nonlinearsolver.FixedPointSolver'>, real_delta=False)¶
Self-consistent real-time iteration for the order parameter.
Adjusts the parameters in the given Geometry object until convergence is met.
Note
Always check that your results are independent of the energy cutoffs, by adjusting the energy range and number of points in the
CurrentSolveryou use.- Parameters:
- solverCurrentSolver
A solver containing the geometry in which to solve for
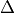
- max_iterationsint, optional
Maximum number of iterations to make
- output_funcfunc(message), optional
Function to use for printing messages. If omitted, prints to stderr.
- iterator
Fixed-point iteration accellerator. Suitable choices are FixedPointSolver (Broyden solver, default) and DummyFixedPointSolver (simple fixed-point iteration).
- real_deltabool, optional
Whether to enforce real-valued order parameter
- Yields:
- kint
Number of current iteration
- dfixed-point solver object
Has the methods residual_norm() that returns a max-norm estimating the error in
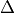 , and relative_residual_norm() that returns
the norm scaled by the initial norm.
, and relative_residual_norm() that returns
the norm scaled by the initial norm.- vfloat
Amount by which current conservation is violated.
Notes
In real-time iteration, some care must be taken to choose the energy grid so that it is sufficiently dense in the energy range where the peak in the
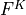 -function will be.
-function will be.The energy cutoff is eliminated by using the formula:
![\Delta = [\int_0^{\epsilon_0}d\epsilon F^K_0(\epsilon)]^{-1} \left(
\Delta_0 \int_0^{\epsilon_0}d\epsilon F^K(\epsilon)
+ \int_{\epsilon_0}^{\omega_c}d\epsilon
[\Delta_0 F^K(\epsilon) - \Delta F^K_0(\epsilon)]
\right)](_images/math/f4fbee191985f3f95bb6f1175199eb7539fc172b.png)
and in the latter term taking the bulk expressions for
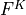 and
and 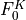 , the latter being the bulk function corresponding to
, the latter being the bulk function corresponding to
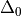 (the bulk gap). Here,
(the bulk gap). Here, 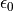 is the energy
limit up to which numerical solutions are calculated for
is the energy
limit up to which numerical solutions are calculated for 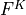 .
.Examples
solver = CurrentSolver(geometry) it = self_consistent_realtime_iteration(solver) for k, d, v in it: if d.residual_norm() < 0.1 and v < 1e-4: break else: raise RuntimeError("Iteration did not converge")
- usadel1.self_consistent_matsubara_iteration(geometry, max_iterations=100, max_ne=300, output_func=<built-in method write of _io.TextIOWrapper object>, iterator=<class 'usadel1.nonlinearsolver.FixedPointSolver'>, E_max=None, force_integral=False, real_delta=False, cutoff_elimination=True)¶
Self-consistent Matsubara iteration for the order parameter.
Adjusts the parameters in the given Geometry object until convergence is met. Applicable only to equilibrium situations.
Note
Always check that your results are independent of the energy cutoffs, by adjusting the max_ne and E_max parameters.
- Parameters:
- geometryGeometry
The geometry in which to solve for
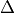
- max_iterationsint, optional
Maximum number of iterations to make
- max_neint, optional
Number of Matsubara frequencies to sum over.
Note
If the number of frequencies given is smaller than that required to sum to frequencies over
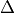 , an energy integral
is performed instead of a discrete sum.
, an energy integral
is performed instead of a discrete sum.- output_funcfunc(message), optional
Function to use for printing messages. If omitted, prints to stderr.
- iterator
Fixed-point iteration accellerator. Suitable choices are FixedPointSolver (Broyden solver, default) and DummyFixedPointSolver (simple fixed-point iteration).
- E_maxfloat
Cutoff energy to use (smaller than Debye, but larger than energy scales of the structure).
If
None, determined automatically. The automatic cutoff satisfies: - It is no larger thanomega_D. - The corresponding length scale is smaller than 0.05 of shortest wireor 0.1 of coherence length
- force_integralbool
Force integration, even if max_ne is large enough for summing up to E_max.
- real_deltabool, optional
Whether to enforce real-valued order parameter
- cutoff_eliminationbool, optional
Whether to perform cutoff elimination. Default: true
- Yields:
- kint
Number of current iteration
- dfixed-point solver object
Has the methods residual_norm() that returns a max-norm estimating the error in
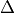 , and relative_residual_norm() that returns
the norm scaled by the initial norm.
, and relative_residual_norm() that returns
the norm scaled by the initial norm.- vfloat
Amount by which current conservation is violated. (NB: not currently implemented in Matsubara iteration, always zero.)
Notes
The energy cutoff is eliminated by using the formula:
![\Delta = [\sum_{\omega_k < \epsilon_0} F_0(\omega_k)]^{-1} \left(
\Delta_0 \sum_{\omega_k < \epsilon_0} F(\omega_k)
+ \sum_{\epsilon_0 < \omega_k < \omega_c} [\Delta_0 F(\omega_k) - \Delta F_0(\omega_k)]
\right)](_images/math/88f093357911cc9b6a57fc81d17951720de33f11.png)
and in the latter term taking the bulk expressions for
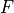 and
and 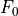 , the latter being the bulk function corresponding to
, the latter being the bulk function corresponding to
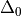 (the bulk gap). Here,
(the bulk gap). Here, 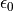 is the energy
limit up to which numerical solutions are calculated for F.
is the energy
limit up to which numerical solutions are calculated for F.Examples
it = self_consistent_matsubara_iteration(geometry) for k, d, v in it: if d.residual_norm() < 0.1 and v < 1e-4: break else: raise RuntimeError("Iteration did not converge")
HDF5 file layout¶
The HDF5 files produced by CurrentSolver.save() have the layout:
/geometry/w_type
/geometry/t_type
...
/spectral/a
/spectral/b
...
/kinetic/fL
/kinetic/fT
...
/coefficient/DL
/coefficient/DT
...
i.e. the attributes of the Geometry, SpResult,
KinResult, and KineticCoefficient objects are simply dumped
to the file to an appropriate place.
You can easily load the HDF5 files by using the supplied h5load.m script
(probably requires a recent version of Matlab).
See also
